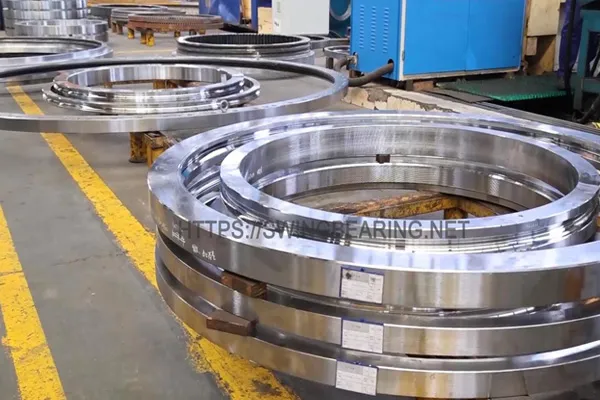

Svelare la potenza nascosta: Individuazione dell'anello di rotazione in un escavatore
La ralla (anello di rotazione), nota anche come cuscinetto di oscillazione, è un componente fondamentale di un escavatore. Si trova alla base della struttura superiore dell'escavatore e consente alla struttura superiore di ruotare rispetto al sottocarro. La ralla è responsabile del trasferimento del peso della struttura superiore e delle forze di scavo al sottocarro. Inoltre, consente all'escavatore di oscillare da un lato all'altro.

Ralla dell'escavatore
Il ralla, a crucial component in an excavator, plays a pivotal role in enabling the machine’s upper structure to rotate smoothly upon its lower structure. Understanding its location is essential for maintenance and repair purposes.
Il cuscinetto oscillante è tipicamente situato alla base della struttura superiore dell'escavatore, dove si interfaccia con la struttura inferiore. È costituito da due anelli concentrici, uno fissato alla struttura superiore e l'altro alla struttura inferiore. Gli anelli sono separati da una serie di elementi volventi, come cuscinetti a sfera o rulli, che facilitano la rotazione.
Per individuare il cuscinetto oscillante, è necessario innanzitutto identificare la struttura superiore e inferiore dell'escavatore. La struttura superiore è la parte che ospita la cabina, il braccio e il braccio, mentre la struttura inferiore comprende i cingoli o le ruote e il sottocarro.
Una volta identificate le strutture superiori e inferiori, cercate il punto in cui si collegano. In genere si tratta di un'apertura circolare o esagonale al centro della struttura superiore. La ralla si trova all'interno di questa apertura.
In alcuni escavatori, il cuscinetto oscillante può essere parzialmente o completamente racchiuso da un alloggiamento protettivo. Questo alloggiamento serve a mantenere la ralla pulita e lubrificata, prolungandone la durata. Per accedere alla ralla, può essere necessario rimuovere l'alloggiamento.
La posizione della ralla può variare leggermente a seconda del modello di escavatore e del produttore. Tuttavia, in genere si trova alla base della struttura superiore, dove fornisce un collegamento stabile e affidabile tra la struttura superiore e quella inferiore.
La conoscenza della posizione della ralla è fondamentale per le operazioni di manutenzione e riparazione. L'ispezione e la lubrificazione regolari della ralla sono essenziali per garantirne il corretto funzionamento e prevenire l'usura prematura o i guasti. Sapendo dove trovare la ralla, i tecnici possono eseguire queste operazioni in modo efficiente, massimizzando le prestazioni e la longevità dell'escavatore.
Il cuscinetto di rotazione, un componente fondamentale di un escavatore, si trova alla base della struttura superiore, dove si collega alla struttura inferiore. Questo posizionamento strategico consente alla struttura superiore di ruotare in modo fluido ed efficiente, permettendo all'escavatore di svolgere un'ampia gamma di attività.
La ralla è composta da due componenti principali: un ingranaggio interno e un ingranaggio esterno. L'ingranaggio interno è fissato alla struttura superiore, mentre l'ingranaggio esterno è fissato alla struttura inferiore. Quando l'operatore dell'escavatore attiva il motore di rotazione, l'ingranaggio interno ruota, azionando l'ingranaggio esterno e facendo ruotare la struttura superiore.
The slew ring plays a vital role in the excavator’s functionality. It provides a stable and reliable connection between the upper and lower structures, ensuring smooth and precise rotation. Without a properly functioning slew ring, the excavator would be unable to perform its intended tasks effectively.
La posizione della ralla alla base della struttura superiore non è solo pratica ma anche vantaggiosa. Questo posizionamento consente un facile accesso durante la manutenzione e le riparazioni, riducendo al minimo i tempi di inattività e garantendo il funzionamento continuo dell'escavatore.
Oltre alla sua funzione primaria, la ralla contribuisce anche alla stabilità complessiva dell'escavatore. Fornendo un solido collegamento tra la struttura superiore e quella inferiore, aiuta a distribuire il peso dell'escavatore in modo uniforme, evitando che si ribalti durante il funzionamento.
Inoltre, la posizione della ralla alla base della struttura superiore consente l'installazione di componenti aggiuntivi, come le linee idrauliche e il cablaggio elettrico. Questi componenti sono essenziali per il funzionamento dell'escavatore e vengono fatti passare comodamente attraverso la ralla, garantendone la protezione e la funzionalità.
In conclusione, la ralla è un componente critico di un escavatore, situato alla base della struttura superiore. Il suo posizionamento strategico consente una rotazione fluida, fornisce stabilità e facilita l'installazione di componenti essenziali. La comprensione della funzione e dell'importanza della ralla è fondamentale per garantire il funzionamento efficiente e affidabile di un escavatore.
The slewing ring is a vital component in an excavator, playing a pivotal role in enabling the upper structure to rotate smoothly upon the undercarriage. Understanding its location, structure, and function is essential for troubleshooting common issues related to this critical part. This detailed guide will help you identify, diagnose, and resolve problems associated with the slewing ring, ensuring your excavator operates efficiently.
The slewing ring is typically situated at the base of the excavator’s upper structure, where it interfaces with the lower frame. It comprises two concentric rings: one fixed to the upper structure and the other to the lower frame. Between these rings are rolling elements, such as ball bearings or rollers, that facilitate the rotation of the upper structure.
To access the slewing ring, it is necessary to remove the upper structure from the undercarriage. This involves several steps:
Once the upper structure is detached, the slewing ring becomes visible as a large, circular component located at the base of the upper frame.
The primary function of the slewing ring is to facilitate the rotation of the excavator’s upper structure relative to its undercarriage. This allows the operator to maneuver the boom, arm, and bucket with precision, enhancing the excavator’s versatility and efficiency. The slewing ring must withstand significant loads and stresses during operation, making its proper maintenance and functioning critical.
One of the most common issues with the slewing ring is excessive wear. This can result from various factors, including heavy usage, inadequate lubrication, and contamination. Symptoms of excessive wear include:
To diagnose excessive wear, perform the following checks:
If excessive wear is confirmed, take the following steps:
Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of the slewing ring. Inadequate or incorrect lubrication can lead to increased friction, overheating, and premature failure.
Signs of lubrication problems include:
To resolve lubrication issues:

Cuscinetti di rotazione per escavatori
Bearing failure in the slewing ring can have severe consequences, including total operational shutdown. This issue can be caused by various factors, including overloading, poor maintenance, and manufacturing defects.
Symptoms of bearing failure include:
If bearing failure is suspected:
Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for preventing issues with the slewing ring and ensuring its optimal performance.
Perform scheduled inspections to identify potential issues before they become severe:
Ensure that operators and maintenance personnel are adequately trained:
The slewing ring is a critical component of an excavator, enabling the upper structure to rotate smoothly upon the undercarriage. Understanding its location, structure, and function is essential for troubleshooting common issues and ensuring optimal performance. By regularly inspecting, maintaining, and addressing issues such as excessive wear, lubrication problems, and bearing failure, you can prolong the life of the slewing ring and enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of your excavator.
By following these detailed maintenance practices, you can ensure that your excavator’s hydraulic system remains in top condition, providing reliable performance and longevity. Regular monitoring, proper lubrication, and timely replacement of worn components are key to preventing common issues and maintaining the efficiency of the slewing ring.
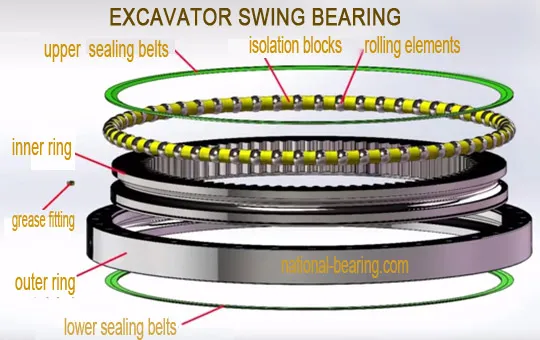
La struttura della ralla
1. Dove si trova la ralla in un escavatore?
- La ralla si trova tra la struttura superiore e quella inferiore dell'escavatore.
2. Qual è la funzione della ralla in un escavatore?
- La ralla consente alla struttura superiore dell'escavatore di ruotare rispetto alla struttura inferiore.
3. Quali sono i diversi tipi di ralle utilizzate negli escavatori?
- Esistono due tipi principali di ralle utilizzate negli escavatori: le ralle a sfere e le ralle a rulli.
La ralla, nota anche come cuscinetto di rotazione, è un componente fondamentale situato alla base della struttura superiore di un escavatore. Fornisce supporto e permette alla struttura superiore di ruotare agevolmente sulla struttura inferiore, consentendo all'escavatore di eseguire operazioni di scavo e di sbancamento con precisione ed efficienza.