
Dévoiler la puissance cachée : Localiser la couronne d'orientation d'une pelleteuse
La couronne d'orientation(slew ring), également connue sous le nom de swing bearing,est un composant essentiel d'une excavatrice. Elle est située à la base de la structure supérieure de la pelle et permet à cette dernière de tourner par rapport au châssis. La couronne d'orientation est chargée de transférer le poids de la structure supérieure et les forces de creusement au train de roulement. Elle permet également à l'excavatrice de se balancer d'un côté à l'autre.

Couronne d'orientation de pelleteuse
Les couronne d'orientation, a crucial component in an excavator, plays a pivotal role in enabling the machine’s upper structure to rotate smoothly upon its lower structure. Understanding its location is essential for maintenance and repair purposes.
Le palier oscillant est généralement situé à la base de la structure supérieure de l'excavateur, où il fait interface avec la structure inférieure. Il se compose de deux anneaux concentriques, l'un fixé à la structure supérieure et l'autre à la structure inférieure. Les anneaux sont séparés par une série d'éléments roulants, tels que des roulements à billes ou des rouleaux, qui facilitent la rotation.
Pour localiser le palier d'oscillation, commencez par identifier les structures supérieure et inférieure de l'excavatrice. La structure supérieure est la partie qui abrite la cabine, la flèche et le bras, tandis que la structure inférieure comprend les chenilles ou les roues et le châssis.
Une fois les structures supérieure et inférieure identifiées, recherchez le point où elles se rejoignent. Il s'agit généralement d'une ouverture circulaire ou hexagonale au centre de la structure supérieure. La couronne d'orientation est située dans cette ouverture.
Dans certaines excavatrices, le palier d'orientation peut être partiellement ou entièrement entouré d'un carter de protection. Ce carter permet de maintenir la bague d'orientation propre et lubrifiée, ce qui prolonge sa durée de vie. Pour accéder à la bague d'orientation, il peut être nécessaire de retirer le carter.
L'emplacement de la couronne d'orientation peut varier légèrement en fonction du modèle et du fabricant de la pelle. Toutefois, elle se trouve généralement à la base de la structure supérieure, où elle assure une connexion stable et fiable entre les structures supérieure et inférieure.
Il est essentiel de connaître l'emplacement de la couronne d'orientation pour les opérations d'entretien et de réparation. L'inspection et la lubrification régulières de la couronne d'orientation sont essentielles pour garantir son bon fonctionnement et éviter une usure prématurée ou une défaillance. En sachant où se trouve la couronne d'orientation, les techniciens peuvent effectuer efficacement ces tâches, maximisant ainsi les performances et la longévité de la pelle.
Le palier oscillant, un composant essentiel d'une excavatrice, est situé à la base de la structure supérieure, où il est relié à la structure inférieure. Cet emplacement stratégique permet à la structure supérieure de tourner en douceur et efficacement, ce qui permet à l'excavatrice d'effectuer un large éventail de tâches.
La couronne d'orientation se compose de deux éléments principaux : un engrenage intérieur et un engrenage extérieur. L'engrenage intérieur est fixé à la structure supérieure, tandis que l'engrenage extérieur est fixé à la structure inférieure. Lorsque l'opérateur de l'excavatrice active le moteur d'orientation, la roue intérieure tourne, entraînant la roue extérieure et faisant tourner la structure supérieure.
The slew ring plays a vital role in the excavator’s functionality. It provides a stable and reliable connection between the upper and lower structures, ensuring smooth and precise rotation. Without a properly functioning bague d'orientation, the excavator would be unable to perform its intended tasks effectively.
L'emplacement de la couronne d'orientation à la base de la structure supérieure est non seulement pratique mais aussi avantageux. Cet emplacement permet un accès facile lors de l'entretien et des réparations, ce qui minimise les temps d'arrêt et garantit le fonctionnement continu de l'excavatrice.
Outre sa fonction première, la couronne d'orientation contribue également à la stabilité générale de la pelle. En assurant une liaison solide entre les structures supérieure et inférieure, elle aide à répartir uniformément le poids de l'excavatrice, l'empêchant ainsi de basculer pendant son fonctionnement.
En outre, l'emplacement de la couronne d'orientation à la base de la structure supérieure permet l'installation de composants supplémentaires, tels que les conduites hydrauliques et le câblage électrique. Ces composants sont essentiels au fonctionnement de l'excavatrice et sont commodément acheminés à travers la couronne d'orientation, ce qui garantit leur protection et leur fonctionnalité.
En conclusion, la couronne d'orientation est un composant essentiel d'une excavatrice, situé à la base de la structure supérieure. Son emplacement stratégique permet une rotation en douceur, assure la stabilité et facilite l'installation de composants essentiels. Il est essentiel de comprendre la fonction et l'importance de la couronne d'orientation pour garantir le fonctionnement efficace et fiable d'une excavatrice.
The slewing ring is a vital component in an excavator, playing a pivotal role in enabling the upper structure to rotate smoothly upon the undercarriage. Understanding its location, structure, and function is essential for troubleshooting common issues related to this critical part. This detailed guide will help you identify, diagnose, and resolve problems associated with the slewing ring, ensuring your excavator operates efficiently.
The slewing ring is typically situated at the base of the excavator’s upper structure, where it interfaces with the lower frame. It comprises two concentric rings: one fixed to the upper structure and the other to the lower frame. Between these rings are rolling elements, such as ball bearings or rollers, that facilitate the rotation of the upper structure.
To access the slewing ring, it is necessary to remove the upper structure from the undercarriage. This involves several steps:
Once the upper structure is detached, the slewing ring becomes visible as a large, circular component located at the base of the upper frame.
The primary function of the slewing ring is to facilitate the rotation of the excavator’s upper structure relative to its undercarriage. This allows the operator to maneuver the boom, arm, and bucket with precision, enhancing the excavator’s versatility and efficiency. The slewing ring must withstand significant loads and stresses during operation, making its proper maintenance and functioning critical.
One of the most common issues with the slewing ring is excessive wear. This can result from various factors, including heavy usage, inadequate lubrication, and contamination. Symptoms of excessive wear include:
To diagnose excessive wear, perform the following checks:
If excessive wear is confirmed, take the following steps:
Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of the slewing ring. Inadequate or incorrect lubrication can lead to increased friction, overheating, and premature failure.
Signs of lubrication problems include:
To resolve lubrication issues:

Palier d'orientation de pelleteuse
Bearing failure in the slewing ring can have severe consequences, including total operational shutdown. This issue can be caused by various factors, including overloading, poor maintenance, and manufacturing defects.
Symptoms of bearing failure include:
If bearing failure is suspected:
Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for preventing issues with the slewing ring and ensuring its optimal performance.
Perform scheduled inspections to identify potential issues before they become severe:
Ensure that operators and maintenance personnel are adequately trained:
The slewing ring is a critical component of an excavator, enabling the upper structure to rotate smoothly upon the undercarriage. Understanding its location, structure, and function is essential for troubleshooting common issues and ensuring optimal performance. By regularly inspecting, maintaining, and addressing issues such as excessive wear, lubrication problems, and bearing failure, you can prolong the life of the slewing ring and enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of your excavator.
By following these detailed maintenance practices, you can ensure that your excavator’s hydraulic system remains in top condition, providing reliable performance and longevity. Regular monitoring, proper lubrication, and timely replacement of worn components are key to preventing common issues and maintaining the efficiency of the slewing ring.
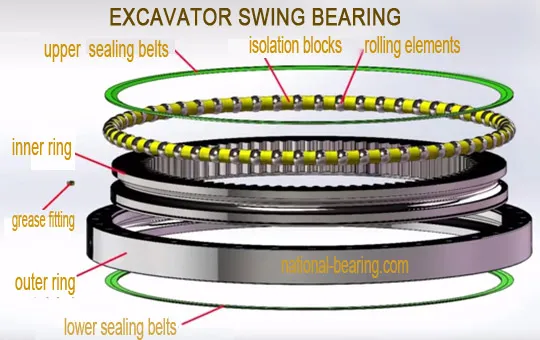
La structure de la couronne d'orientation
1. Où se trouve la couronne d'orientation dans une excavatrice ?
- La couronne d'orientation est située entre les structures supérieure et inférieure de l'excavateur.
2. Quelle est la fonction de la couronne d'orientation dans une excavatrice ?
- La couronne d'orientation permet à la structure supérieure de l'excavateur de tourner par rapport à la structure inférieure.
3. Quels sont les différents types de couronnes d'orientation utilisés dans les excavateurs ?
- Il existe deux principaux types de couronnes d'orientation utilisées dans les excavateurs : les couronnes d'orientation à roulement à billes et les couronnes d'orientation à roulement à rouleaux.
La couronne d'orientation, également connue sous le nom de palier d'oscillation, est un composant crucial situé à la base de la structure supérieure d'une excavatrice. Elle fournit un support et permet à la structure supérieure de tourner en douceur sur la structure inférieure, ce qui permet à l'excavatrice d'effectuer des opérations de creusement et d'excavation avec précision et efficacité.